What Is Volatile Or Non-Volatile Memory: Explained Simply
What Is Volatile And Nonvolatile Memory ?|| About Volatile Memory || #Volatile #Computer
Keywords searched by users: What is volatile or non-volatile memory Non volatile memory, Volatile memory, Volatile memory là gì, Which is the group non volatile memory, Volatile storage examples, Typically volatile, Volatile in C, Computer memory
What Is Volatile And Non-Volatile Memory?
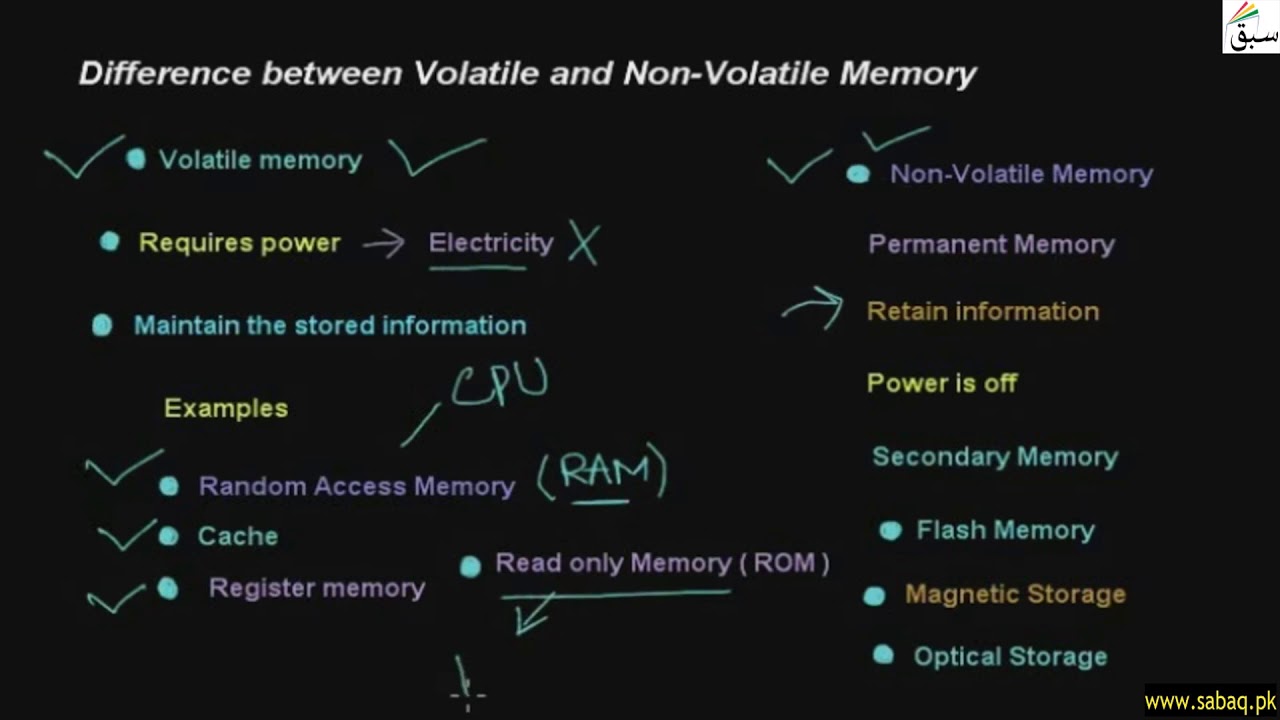
Volatile and non-volatile memory serve crucial roles in computing, each with distinct characteristics. Volatile memory, such as cache memory and RAM, temporarily stores data and computer programs that the CPU requires for real-time operations. However, once a user powers off the computer, volatile memory erases its contents, making it a temporary storage solution. In contrast, non-volatile memory is persistent and retains its data even when the computer is turned off. This type of memory, which includes options like hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs), stores information that persists over time, allowing users to access it even after powering down the computer. These two forms of memory play essential roles in the overall functionality of computers and digital devices.
What Is Volatile Memory?
Volatile memory, often referred to as volatile RAM (Random Access Memory), is a fundamental component of a computer’s architecture. This type of memory is unique in that it retains data only when the device is actively powered and operational. When the power supply to the device is interrupted, whether due to a deliberate shutdown or an unexpected power outage, volatile memory swiftly loses all of its stored information. This characteristic sets it apart from non-volatile memory, such as hard drives or solid-state drives, which can retain data even when the power is turned off. Volatile memory plays a crucial role in a computer’s functioning, as it is where the computer stores the data and programs that it is currently using, allowing for quick access and manipulation of information. However, it’s essential to save important data to non-volatile storage to prevent loss in case of power failure or system shutdown.
What Is An Example Of A Non-Volatile Memory?
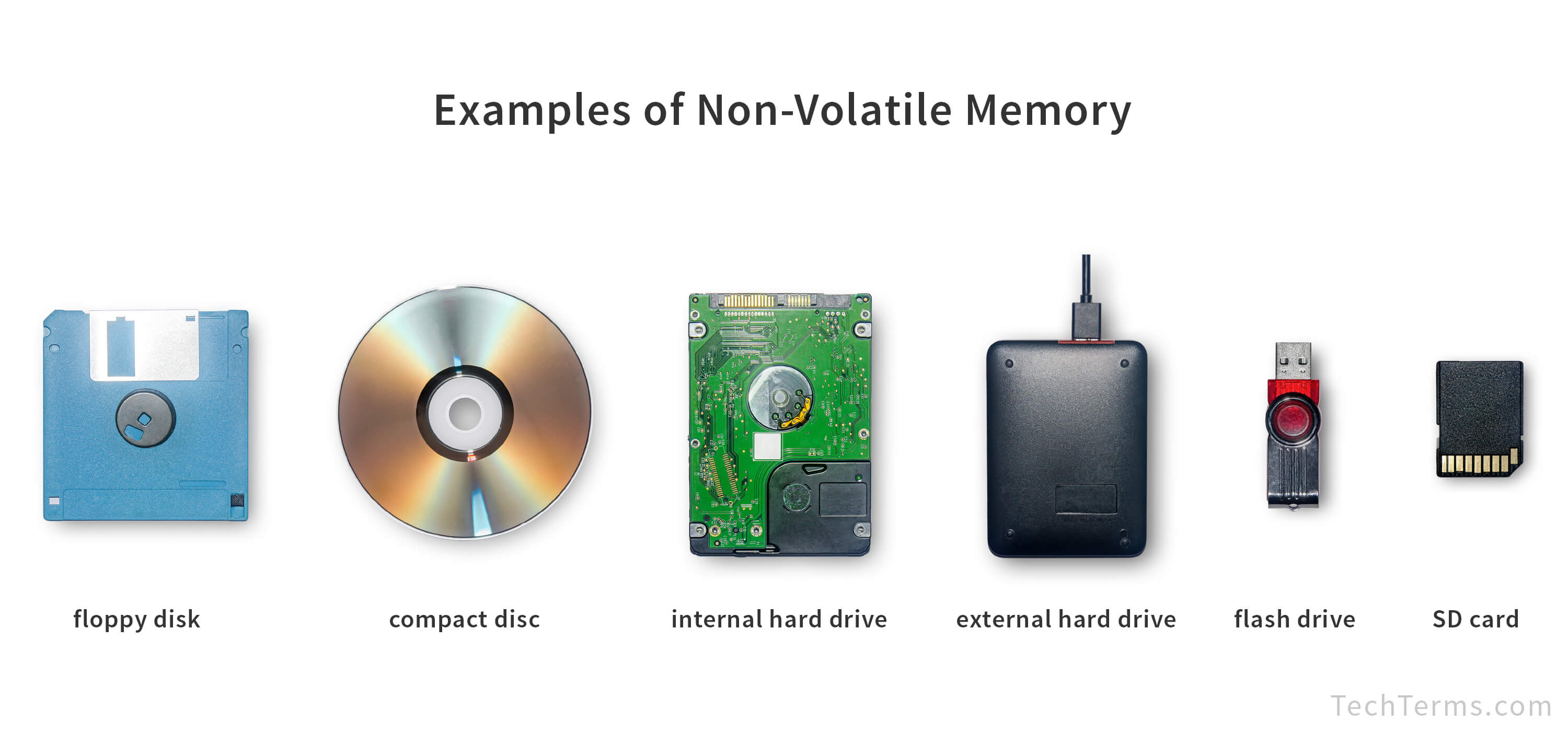
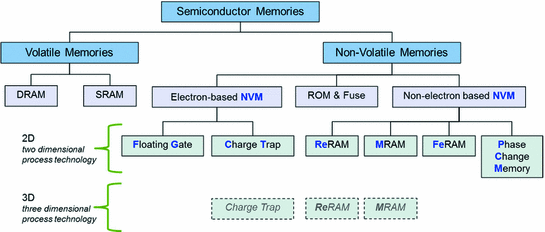
Non-volatile memory refers to a category of computer storage technologies that retain data even when the power is turned off. Several types of non-volatile memory exist, serving various purposes. Examples of non-volatile memory include:
-
Read-Only Memory (ROM): ROM is a type of memory that stores data permanently and cannot be easily altered. It typically contains firmware or software instructions necessary for a device to function, such as a computer’s BIOS.
-
EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM): EPROM is a variant of ROM that allows for data erasure and reprogramming, but it requires exposure to ultraviolet light to erase its contents.
-
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): EEPROM is similar to EPROM but can be electrically erased and reprogrammed, making it more convenient for applications where frequent updates are needed, like storing configuration settings in electronic devices.
-
Ferroelectric RAM: Ferroelectric RAM is a type of non-volatile memory that uses ferroelectric materials to store data. It combines the speed of volatile RAM with non-volatility, making it suitable for applications requiring both speed and data retention.
-
Computer Data Storage Devices: Various computer storage devices, such as hard disk drives, optical discs, floppy disks, and magnetic tape, also fall under the category of non-volatile memory. These technologies store data magnetically or optically, ensuring data persistence even when the power is off.
Non-volatile memory plays a crucial role in preserving data integrity and maintaining device functionality across a wide range of applications, from embedded systems to data storage solutions.
Discover 40 What is volatile or non-volatile memory


Categories: Collect 28 What Is Volatile Or Non-Volatile Memory
See more here: tfvp.org

At a high level, the biggest difference between volatile and non-volatile memory is that volatile memory stores data when a computer is on but erases it as soon as the computer is switched off, whereas non-volatile memory remains in a computer even after the system shuts off.The volatile memory stores data and computer programs that the CPU may need in real-time, and it erases them once a user switches off the computer. Cache memory and RAM are types of Volatile memory. Non-volatile memory, on the other hand, is static. It remains in a computer even after a user switches it off.Volatile memory is a type of memory that maintains its data only while the device is powered. If the power is interrupted for any reason, the data is lost.
Learn more about the topic What is volatile or non-volatile memory.
- Volatile Memory vs. Nonvolatile Memory: What’s the Difference?
- Difference Between Volatile Memory and Non … – BYJU’S
- What is volatile memory? – TechTarget
- Non-volatile memory – Wikipedia
- What is Read-Only Memory (ROM)? – Definition from Techopedia
- Volatile Memory – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
See more: https://tfvp.org/category/science blog
