Which Is The Anomeric Carbon: Unveiling Its Crucial Role
Anomers And Anomeric Effect In Easy Way
Keywords searched by users: Which is the anomeric carbon Anomeric carbon là gì, Anomeric carbon, Epimers, Anomeric pair examples, Furanose, Glycosidic bond, Mutarotation, Epimers definition
What Is An Anomeric Carbon With Example?
Anomeric Carbon: Understanding its Significance with a Sugar Example
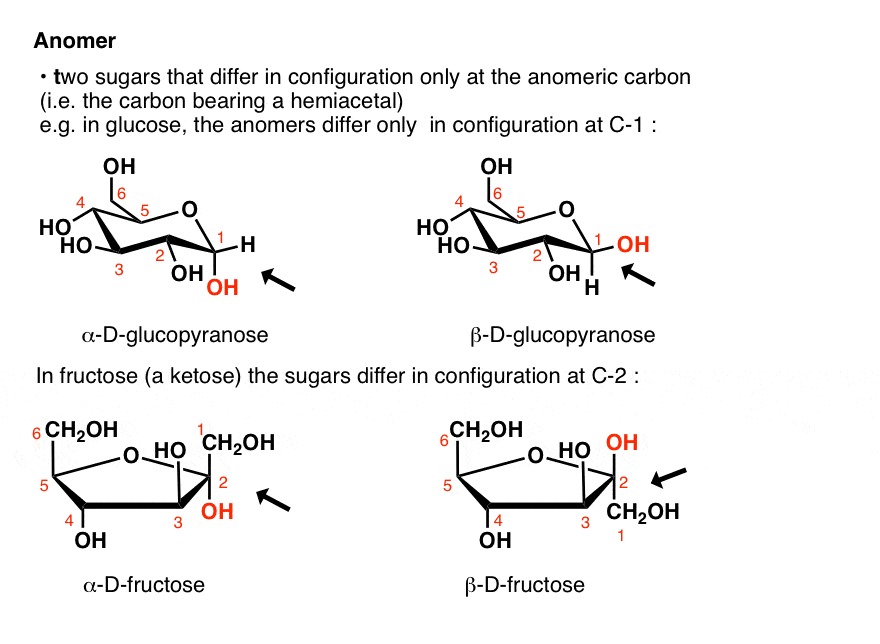
An anomeric carbon is a unique structural feature found in certain organic compounds, notably sugars. In its acyclic form, an anomeric carbon is not a stereocenter, meaning it does not exhibit chiral properties. However, when these compounds adopt a cyclic structure, the anomeric carbon transforms into a stereocenter, acquiring the ability to exist in two different three-dimensional arrangements known as anomers. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in the chemistry of carbohydrates, particularly sugars.
For instance, consider the sugar glucose. In its linear or acyclic form, glucose does not possess a stereocenter at the anomeric carbon position. However, when glucose forms a cyclic structure, such as in the case of the common six-membered ring form called the pyranose ring, the carbon atom in question becomes a stereocenter. This conversion from non-chiral to chiral isomerism is significant in understanding the diverse properties and biological functions of sugars, making anomeric carbons a fundamental concept in carbohydrate chemistry. (Date: December 1, 2021)
Is Anomeric Carbon C1 Or C2?
The position of the anomeric carbon in a molecule, such as glucose when it undergoes cyclization, is a crucial aspect to understand. When glucose transitions into its cyclic form, it undergoes a structural change that introduces a new chiral center at carbon atom C-1. This specific carbon atom, known as the anomeric carbon, plays a pivotal role in the formation of cyclic structures and the overall stereochemistry of the molecule. In summary, during the conversion of glucose to its cyclic form, the carbon atom at position C-1 becomes the anomeric carbon, thus highlighting its significance in the molecular structure.
Is C1 The Anomeric Carbon?
Is C1 the anomeric carbon? To clarify, in the cyclic form of a sugar, the anomeric carbon is the one that previously belonged to the carbonyl group when the sugar was in its linear, straight-chain structure. When the sugar molecule undergoes a transformation into a ring structure, carbon atom C-1 assumes a new role as a chiral center. Therefore, in this context, C-1 indeed represents the anomeric carbon. This information was discussed on July 22, 2015.
Collect 48 Which is the anomeric carbon





Categories: Update 51 Which Is The Anomeric Carbon
See more here: tfvp.org

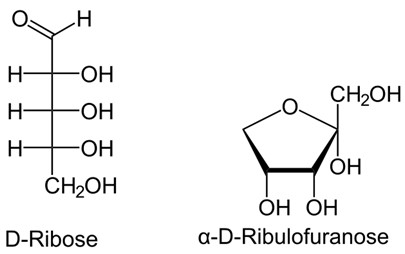
An anomeric carbon can be identified as the carbonyl carbon (of the aldehyde or ketone functional group) in the open-chain form of the sugar. It can also be identified as the carbon bonded to the ring oxygen and a hydroxyl group in the cyclic form.In carbohydrate chemistry, diastereomers differing only at the hemiacetal or acetal carbon are called anomers, and the hemiacetal or acetal carbon atom is called the anomeric carbon atom. 𝛼-form & 𝛽-form, are called anomers. Thus C1 carbon becomes the anomeric carbon of glucose in its pyranose form.Anomeric Carbon Defined
An anomeric carbon is a carbon that, in the acyclic form, is not a stereocenter, but once it takes on the cyclic form, it becomes a stereocenter. Sugars are the perfect example of this.
Learn more about the topic Which is the anomeric carbon.
- Anomeric Carbon | Definition & Effect – Study.com
- Which carbon becomes the anomeric carbon of glucose in its pyranose …
- Anomeric Carbon: Definition & Overview – Video & Lesson Transcript
- Epimers And Anomers – Carbohydrates – MCAT Content
- What do you mean by an anomeric carbon? I want … – Socratic
- Anomeric Carbon | Definition & Effect – Video & Lesson Transcript
See more: blog https://tfvp.org/category/science